Definition
The man-in-the-middle attack (often abbreviated MITM), or bucket-brigade attack, or sometimes Janus attack, is a form of active eavesdropping in which the attacker makes independent connections with the victims and relays messages between them, making them believe that they are talking directly to each other over a private connection when in fact the entire conversation is controlled by the attacker. The attacker must be able to intercept all messages going between the two victims and inject new ones, which is straightforward in many circumstances (for example, an attacker within a few miles of an unencrypted Wi-Fi wireless access point, can insert himself as a man-in-the-middle).
A man-in-the-middle attack can only be successful when the attacker can impersonate each endpoint to the satisfaction of the other. Most cryptographic protocols include some form of endpoint authentication specifically to prevent MITM attacks. For example, SSL authenticates the server using a mutually trusted certification authority.
For more information, please click link below :-
- Wikipedia
- Search Security
- Wise Geek
- Security Focus
- owasp
How does the MiTM attack?
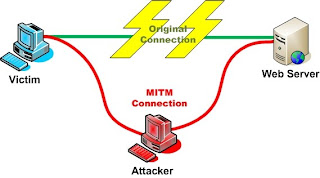
Man in the middle attacks are one of the several devices that are used to gain access to proprietary information, such as pass codes, login credentials, and credit card numbers. The process essentially involves establishing a virus that acts as the interface between two points. Neither party in the exchange is aware that the information that is exchanged is intercepted and captured by the intermediate virus.
The concept of a man in the middle attack predates the inception of the personal computer and widespread use of the Internet. Even in earlier days, intelligence operations would employ the idea of establishing a third party who would in effect initiate a dual interface with two other parties. Each of the other two parties would assume they were involved in a direct connection with one another, not realizing that the third party was intercepting, interpreting and then passing on the communication.
Click here to download on how to defend yourself from Man In The Middle Attack.
Click here to download documentation concepts of Man In The Middle Attack.
 How to crack Windows local password?
How to crack Windows local password?